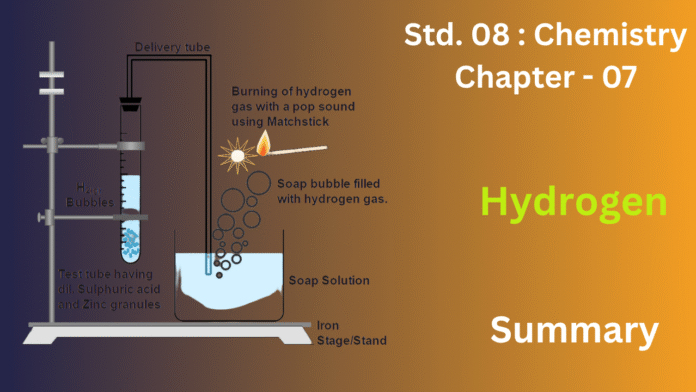
Hydrogen, the universe’s most abundant and lightest element, is typically found in compounds like water on Earth due to its high reactivity. It can be prepared in the lab by reacting dilute acids with active metals such as zinc, or industrially through water electrolysis or the Bosch process.
Chemically, it forms water when combusting with oxygen, acts as a reducing agent (e.g., with metal oxides), and reacts with both metals (forming hydrides) and non-metals (like chlorine and nitrogen in the Haber process).
Hydrogen’s applications are diverse, spanning rocket fuel, future clean energy, vegetable oil hydrogenation, and the production of ammonia and hydrochloric acid. It also serves as a reducing agent in metallurgy and is used in oxy-hydrogen flames for cutting and welding. Due to its explosive nature when mixed with air, safety is paramount.
Exercise
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Hydrogen is _________ than air.
Ans : lighter
(b) Hydrogen is_________soluble in water.
Ans : sparingly
(c) Hydrogen bums with an oxyhydrogen ________ flame and ___ sound is heard.
Ans : pale blue,pop
(d) A metal ____________ hydrogen in the reactivity series gives hydrogen with water.
Ans : sodium
(e) Hydrogen reacts with metal oxides to form _________.
Ans : metal and water
(f) Oxidation is the removal of _________and addition of ___________.
Ans : hydrogen ,oxygen
(g) In redox reaction oxidation and reduction occur __________.
Ans : simultaneously
2. Indicate which of the following statements are true and which are false:
(a) Hydrogen molecule is monovalent.
(b) The removal of hydrogen from a substance is called reduction.
(c) Nitric acid can not be used to prepare hydrogen by its action on active metals ?
(d) The reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is reversible.
(e) Zinc can liberate hydrogen from water, acid and alkali solution.
(f) Hydrogen is combustible as well as a supporter of combustion.
(g) Hydrogen gas is easily liquefiable.
Answer:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) False. Hydrogen cannot be prepared by the action of nitric acid on metals because it also releases nitrous oxide and nitric oxide.
(d) True
(e) True
(f) False
(g) False
3. Complete and balance the following equations:
Answer:
4. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Hydrogen be used as a fuel?
(b) Though hydrogen is lighter than air it cannot be collected by downward displacement of air.
(c) A pop sound produced when hydrogen is burnt?
(d) Helium replaced hydrogen in weather observation balloons?
(e) Nitric acid not used for the preparation of hydrogen gas?
(a) Because of its high heat of combustion, it is used as a fuel.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen as a promising fuel: Hydrogen is a highly attractive fuel for the future. It’s incredibly energy-dense, and its combustion product is simply water, making it a clean and environmentally friendly option.
(b) Hydrogen’s low density: Hydrogen is exceptionally lightweight, significantly less dense than air. This property causes it to rise and disperse rapidly, making conventional collection methods quite difficult.
(c) “Pop” sound of burning hydrogen: The characteristic “pop” sound heard when hydrogen burns is a result of its swift reaction with oxygen.
(d) Helium’s use in weather balloons: Despite hydrogen’s superior lifting power, its high flammability makes it unsafe for weather balloons. Helium is the preferred choice because it’s non-combustible and unreactive, offering a safer alternative even if it provides slightly less lift.
(e) Why nitric acid isn’t used for hydrogen production: Nitric acid is typically not used to produce hydrogen because it acts as a strong oxidizing agent. Instead of simply releasing hydrogen gas, it tends to oxidize the newly formed hydrogen into water and also generates problematic nitrogen oxide gases. For cleaner hydrogen production, dilute sulfuric or hydrochloric acids are favored as they lack this strong oxidizing effect.
5. Name the following:
(a) Two metals which give hydrogen with cold water.
(b) A metal which liberates hydrogen only when steam is passed over red hot metal.
(c) The process in which oxygen is added or hydrogen is removed.
(d) A metallic oxide which can be reduced into metal by hydrogen.
Answer:
(a) Sodium and potassium are vigorous; they instantly react with cold water, giving off hydrogen gas.
(b) Iron is less reactive, only releasing hydrogen when encountering hot steam.
(c) Oxidation is essentially adding oxygen or stripping away hydrogen.
(d) Hydrogen can reverse metal oxides like copper or lead oxide, turning them back into pure metal.
6. (a) Name the chemicals required to prepare hydrogen
gas in the laboratory.
(b) Give a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
(c) Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen.
(d) How is hydrogen gas collected?
Answer:
(a) To prepare hydrogen gas in the lab, you’ll need granulated zinc and either dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid.
(b) The balanced chemical equation for hydrogen gas preparation using dilute hydrochloric acid is: Zn(s)+2HCl(aq)→ZnCl2(aq)+H2(g)
(c)
(d) Collection method: This method is used because hydrogen is nearly insoluble in water and much lighter than air, allowing it to bubble up and displace the water in the inverted gas jar.
7. How would you show that hydrogen:
(a) is a non-supporter of combustion?
(b) is lighter than air?
Answer:
(a) When hydrogen burns, it uses up the oxygen a candle needs to stay lit, effectively extinguishing the flame. So, hydrogen burns on its own but doesn’t support other fires; it puts them out by consuming their oxygen.
(b) A balloon filled with pure hydrogen floats upwards because hydrogen is less dense than air. This happens because hydrogen molecules are much lighter than the nitrogen and oxygen molecules that make up most of the air, a property that was once used in hydrogen-filled airships.
8. Hydrogen is a good reducing agent: What do you understand by the above statement? Explain with the help of copper oxide as an example.
Answer:
Hydrogen is an effective reducing agent because it readily removes oxygen from other compounds. For example, when hydrogen gas passes over heated black copper oxide (CuO), it takes the oxygen, yielding reddish-brown pure copper (Cu) and water (H₂O) as steam.
In this reaction:
- Copper oxide is reduced to copper (loses oxygen).
- Hydrogen is oxidized to water (gains oxygen).
9. (a) Name a process by which hydrogen gas is manufactured.
(b) Give equations for the reactions.
(c) How is hydrogen separated from carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide?
Answer:
(a) One common process by which hydrogen gas is manufactured is Steam Reforming of Natural Gas.
(b) Equations for the reactions:
Reaction of methane with steam (primary reaction):
CO(g)+H2O(g)⇌CO2(g)+H2(g)
(c) Separation of hydrogen from carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): It is usually removed by scrubbing using chemical absorbents like potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃) or amines, which selectively absorb CO₂.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): This is often removed by passing the gas mixture over a catalyst in the water-gas shift reaction (as shown above), converting it to carbon dioxide and more hydrogen. Any remaining CO can be removed through pressure swing adsorption (PSA) or methanation, where CO is reacted with hydrogen to form methane and water:
10. Match the statements in Column A with those in Column B.
Answer:
11. State four uses of hydrogen:
Answer:
Here are four common uses of hydrogen:
- Production of Ammonia (Haber-Bosch Process): A significant amount of hydrogen is used to synthesize ammonia (NH3), which is a crucial component in the manufacturing of fertilizers.
- Fuel in Rockets and Fuel Cells: Due to its high energy content per unit mass, hydrogen serves as a powerful rocket fuel. It is also used in fuel cells to generate electricity with water as the only byproduct, making it a promising clean energy source for vehicles and stationary power.
- Hydrogenation of Oils: In the food industry, hydrogen is used to convert unsaturated vegetable oils into saturated fats (e.g., in the production of margarine and vanaspati ghee), a process called hydrogenation.
- Petroleum Refining: Hydrogen is extensively used in oil refineries to remove impurities like sulfur from crude oil and to produce various petroleum products such as gasoline and diesel through processes like hydrocracking.
12. Define:
(a) catalytic hydrogenation (b) oxidation
(c) reduction (d) redox reaction
Answer:
(a) Catalytic Hydrogenation: This process adds hydrogen to molecules with double or triple bonds, converting them to single bonds. A metal catalyst (like platinum) accelerates the reaction without being used up.
(b) Oxidation: This is when a substance gains oxygen, loses hydrogen, or loses electrons. Rusting of iron is a common example.
(c) Reduction: The reverse of oxidation reduction involves a substance losing oxygen, gaining hydrogen, or gaining electrons.
(d) Redox Reaction: This describes a chemical reaction where one substance is oxidized (loses electrons) while another is simultaneously reduced (gains electrons). They always happen together.
13. Multiple Choice Questions
(a) Equal volumes of hydrogen and chlorine are exposed to diffused sunlight to prepare
- hydrogen chloride
- water
- sodium hydroxide
- hydrochloric acid
Ans : hydrogen chloride
(b) The metal which reacts with cold water to produce hydrogen is
- magnesium
- aluminium
- calcium
- iron
Ans : calcium
(c) In metal activity series the more reactive metals are at
- top
- bottom
- middle
- none
Ans : top
(d) Hydrogen is responsible for producing
- heat and light
- hydrogenated oil
- fertilizers
- all of the above
Ans : all of the above
(e) Hydrogen is
- combustible
- non-combustible
- supporter of combustion
- neither supporter nor combustible
Ans : combustible
(f) Water gas is a mixture of
- carbon monoxide and oxygen
- carbon monoxide and hydrogen
- hydrogen and oxygen
- hydrogen and nitrogen.
Ans : carbon monoxide and hydrogen