Minerals are natural ingredients of the Earth, each unique in its chemistry and physical characteristics. Rocks are essentially a blend of these minerals.
When a mineral holds a metal that we can extract and make money from, it earns the title of an ore. A good example is bauxite, which is an ore because it’s a profitable source of aluminum. So, while every ore is a mineral, not every mineral is valuable enough to be an ore.
We can group minerals into two main types: metallic ones, like iron, copper, and gold, and non-metallic ones, such as coal, petroleum, and mica.
South America is rich in mineral resources. Brazil has a lot of iron ore. Chile is a major source of copper. If you’re looking for bauxite to make aluminum, check out Brazil and Guyana. Peru and Bolivia were important for silver. Gold is found in several countries, and Venezuela is famous for its oil. The continent also has other valuable minerals like tin, lead, zinc, and even precious stones, all playing a big part in the economies of its countries.
EXERCISES
A. Fill in the blanks
- All rocks are composed of———-.
Ans : minerals
- Minerals are obtained by a process called————–.
Ans : mining
- Metallic minerals are generally found in ——— rocks.
Ans : igneous
- Ferrous minerals contain——–.
Ans : iron
- Peat has very little————.
Ans : carbon
B. Write true or false
1. Metals can be profitably extracted from ores.
Answer. True.
2. Metallic minerals are generally found in sedimentary rocks.
Answer. False.
Correct — Metallic minerals are generally found in igneous rocks.
3. Bauxite is the lightest metal.
Answer. True.
4. Bituminous coal has the highest carbon content.
Ans. False.
Correct — Anthracite coal has the highest carbon content.
5. Mica is a metallic mineral.
Ans. False.
Correct— Mica is a non-metallic mineral.
C. Match the columns

Answer:
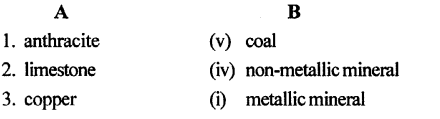
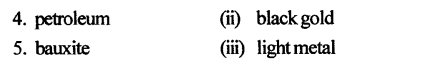
Question 1
What is a mineral?
Answer: Think of it as a naturally formed, solid stuff in the Earth with its own recipe (chemical makeup) and arrangement of atoms (crystal structure).
Question 2. Name a few minerals.
Answer: You’ve got things like quartz (often clear or white), feldspar (common in rocks), mica (thin sheets), calcite (makes up limestone), gypsum (used in plaster), and hematite (an iron mineral).
Question 3. What is an ore?
Answer: Basically, it’s a rock that’s worth digging up because it has enough valuable minerals (usually metals) in it to make it profitable to take them out.
Question 4. What is the main difference between a ferrous and a non-ferrous mineral?
Answer: Ferrous minerals contain iron, while non-ferrous ones do not.
Question 5. Mention any two characteristics of iron ore.
Answer: It’s usually hard and heavy, with a shiny, metallic look.
Question 6. Mention the different types of iron ore.
Answer: The common types are hematite, magnetite, limonite, and siderite.
Question 7. What is surface mining?
Answer: It’s digging out minerals from the top layer of the ground by taking away the soil and rocks above.
Question 8. Mention any three uses of coal.
Answer: Mainly for making electricity, powering factories, and as a base for some chemicals
E. Answer the following questions in one or two paragraphs
Question 1. Differentiate between metallic and non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
| Feature | Metallic Minerals | Non-Metallic Minerals |
| Composition | Contain metal elements (e.g., iron, copper, gold). | Do not contain metal elements (e.g., carbon, sulfur, salt). |
| Luster (Shine) | Have a characteristic metallic shine or luster. | Have a dull, vitreous (glassy), or pearly luster. |
| Conductivity | Excellent conductors of heat and electricity. | Generally poor conductors (insulators). |
| Malleability | Malleable and ductile (can be hammered into sheets or drawn into wires). | Brittle (break or shatter when hit). |
| Occurrence | Usually found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. | Usually found in sedimentary rocks. |
Question 2. Give an account of iron ore production in the world.
Answer: A few big players dominate iron ore production globally, with China and Australia leading the pack. Brazil and India are also significant producers. This ore fuels industries like construction and manufacturing worldwide.
Question 3. Give any three uses of copper.
Answer: Copper’s great for electrical wiring because it conducts electricity really well. It’s also used to make strong alloys like brass for things like plumbing. Plus, it can kill germs, so it’s used in some healthcare settings.
Question 4. What are the two types of mining? Elaborate on the differences between the two.
Answer: The two main ways we dig up minerals are surface mining and underground mining. Surface mining is like a big open pit or stripping away layers when the good stuff is close to the top. It’s cheaper and safer but messes up more land. Underground mining is for when the minerals are way down deep, so we dig tunnels. It costs more and is riskier, but it doesn’t scar the surface as much.
Question 5. Describe the importance of minerals.
Answer: Minerals are super important! They’re the basic stuff we need for almost everything, from building houses and making cars to our phones and power. They’re the foundation of how we live today.
Question 6. Why is it important to conserve minerals?
Answer: We need to save minerals because we can’t make more of them, at least not quickly. Using them wisely means there will be enough for people later on. Plus, it helps protect the environment by reducing the harm that digging them up can cause.
F. Picture study.

Look at this picture of the inside of an iron and steel industry and answer the following questions
Question 1. Which are the major producers of iron and steel in Asia?
Answer: Asia’s top dogs for making iron and steel are China, Japan, India, South Korea, and Russia.
Question 2. Which states in the south of India produce a large quantity of iron and steel?
Answer: Down south in India, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu churn out a lot of iron and steel.


