Its main goals are to maintain peace, foster international relations, and advance social progress and human rights.
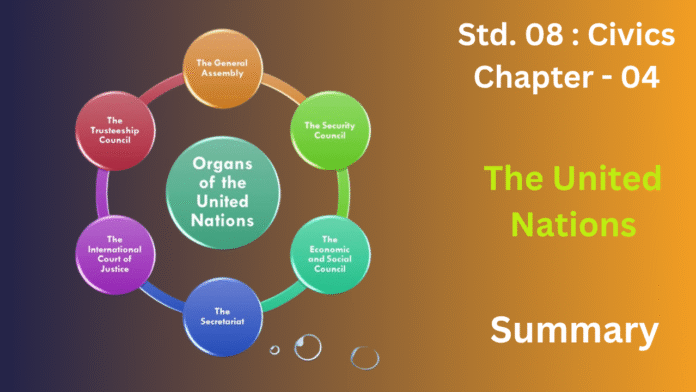
The UN’s core structure includes the General Assembly (its main deliberative body), the Security Council (responsible for peace and security, with five permanent members holding veto power), the Economic and Social Council (addressing global challenges), the International Court of Justice (settling legal disputes), and the Secretariat (the administrative arm led by the Secretary-General).
The UN achieves its goals through various activities like peacekeeping, humanitarian aid, human rights advocacy, and tackling global issues such as poverty and climate change through specialized agencies like UNICEF and WHO.
India has been a significant and active member since the UN’s beginning, contributing extensively to peacekeeping missions and advocating for global causes, demonstrating its commitment to multilateralism and a just world. Essentially, understanding the UN highlights its continuous efforts to create a more peaceful, just, and sustainable world.
I. Fill in the blanks:
- All __________ can become members of the United Nations.
Ans:peace loving nations
- The present number of member-countries in the UNO is_________.
Ans: 193
- One major goal of UNICEF was____________ 1990.
Ans: Universal Child Immunisation against preventable diseases by
- The International Court of Justice settles disputes between______________.
Ans: member states of the United Nations.
- UNESCO came into existence in ________.
Ans:1946
II. Match the content of column A with other of column B
Ans:
III. Answer the following questions:
1)Why and when was the UNO formed?
Ans: The United Nations (UN) was formed on October 24, 1945, following World War II. It was created primarily to prevent another devastating global conflict and to foster international cooperation. The aim was to establish an organization that would maintain peace and security, promote human rights, develop friendly relations among nations, and help countries work together to solve global problems like hunger, disease, and illiteracy. It essentially succeeded the League of Nations, which had failed to prevent World War II.
2)What are the objectives and principles of the UNO?
Ans:The United Nations Organization (UNO) was established to promote global peace and cooperation. Its primary aims are to maintain international peace and security by preventing and resolving conflicts, foster worldwide cooperation on economic, social, cultural, and humanitarian issues while upholding human rights, and act as a central platform for nations to coordinate their efforts.
The UNO operates on fundamental principles including the sovereign equality of all member states, the expectation that members will honor their commitments in good faith, and the mandate for peaceful resolution of disputes. It strictly prohibits the use or threat of force against other nations. Members are required to support UN actions and refrain from assisting states that oppose UN enforcement, with the goal of encouraging even non-member states to adhere to these principles. Generally, the UN avoids intervening in a nation’s internal affairs, except in specific situations requiring enforcement.
3)Name the chief organs of the UNO and list down theirNo member-state shall interfere in the internal affairs of any other member-state functions.
Ans: The six principal organs of the United Nations each play a vital role in global governance. The General Assembly is the main deliberative and policy-making body, while the Security Council is responsible for international peace and security. The International Court of Justice (ICJ) serves as the UN’s primary judicial organ, and the Secretariat handles daily operations. The Trusteeship Council is currently inactive, having completed its mandate.
4)Name the official languages of the UNO.
Ans:The UN operates with six official languages: English, French, Russian, Chinese, Arabic, and Spanish, crucial for accurate global communication and document translation. English and French serve as the additional working languages for the UN Secretariat’s daily operations.
5)How does the UNO manage its funds?
Ans:The UN relies on required financial contributions from its member countries. The General Assembly, acting on advice from the Committee on Contributions, determines these amounts. This committee evaluates each nation’s “capacity to pay” based on factors like gross national income, debt levels, and population figures. This mechanism ensures a consistent financial foundation for the UN’s essential functions and peacekeeping efforts.
6)Describe the UNO Flag. Draw and colour it.
Ans:The light blue United Nations flag prominently displays two olive branches, open at the top, as its central emblem. This universally understood symbol of peace directly reflects the UN’s core mission and its aspirations for global harmony.
7)Name the permanent members of the UNO.
Ans:The five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the United States, the United Kingdom, France, China, and Russia. Their unique and powerful standing within the UN system originates from their role as the primary victorious Allied powers at the conclusion of World War II. The UN Charter, established in 1945, not only granted them permanent seats on the Security Council but also endowed them with the crucial “veto power.”
This veto power allows any one of these five permanent members to block the adoption of any “substantive” resolution put forth in the Security Council, irrespective of the support it may garner from the ten other elected members of the council. While this mechanism was intended to ensure the consensus of major global powers on significant international actions, it has frequently been a subject of considerable debate and criticism. Over the years, its application has often resulted in stalemate and an inability to act on critical global challenges.
Additional Questions
EXERCISES
A. Fill in the blanks:
- The _________ was formed in 1920 after the end of the First World War.
Ans:League of Nations
- Each member state of the UN can send up to _________representatives to the General Assembly.
Ans:Five
- The__________ is often referred to as the ‘Enforcement Wing’ of the UN.
Ans: Security council
- The five permanent members of the Security Council are the ________.
Ans:USA, UK, France, People’s Republic of China and the Russian Federation
- The objective of the ECOSOC is to free the world from ________.
Ans:want
- The WHO is a __________agency of the UN.
Ans:specialized
B. Match the following:
Ans:
C. Choose the correct answer:
- 24 October/22 March/21 June is celebrated as United Nations Day.
Ans. 24 October is celebrated as United Nations Day. - The olive branches on the UN flag symbolize peace/wealth/ truth.
Ans. The olive branches on the UN flag symbolize peace. - The Economic and Social Council consists of 54 members elected by the General Assembly for a 3/4/5-year term.
Ans. The Economic and Social Council consists of 54 members elected by the General Assembly for a 5-year term. - The International Court of Justice is located in New York City in the USA/The Hague in the Netherlands/Paris in France.
Ans. The International Court of Justice is located in The Hague in the Netherlands. - The Secretariat/General Assembly/International Court of Justice is the chief administrative organ of the UN.
Ans. The Secretariat is the chief administrative organ of the UN.
D. State whether the following are true or false:
- All the members of the UN are members of the General Assembly.
Ans: True. - French is one of the official languages of the UN.
Ans:True. - The Trusteeship Council is the most important organ of the UN.
Ans: False
Correct: The Security Council is the most important organ of the UN. - UNESCO and UNICEF are specialized agencies of the UN
Ans: True. - Most of the world’s problems have disappeared with the end of the Cold War.
Ans: False.
Correct: Most of the world’s problems have disappeared with the end of the Cold War. This, however, did not happen.
E. Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
1)Mention one important organ of the UN.
Ans:The Security Council is arguably the UN’s most vital organ due to its primary role in upholding international peace and security. What sets it apart is its unique power to issue binding resolutions, not just recommendations, on member states. This authority allows it to impose sanctions, authorize peacekeeping operations, and even deploy military force, granting it considerable sway in global conflict resolution.
2)Who are the members of the General Assembly?
Ans: The United Nations General Assembly serves as a distinctive global platform where all 193 Member States converge. Its universal membership grants every UN member nation a seat and an equal vote, positioning it as the only organ within the organization that genuinely embodies the international community. In addition to these full members, certain non-member states, like the Holy See and Palestine, are afforded observer status. This enables them to participate in debates and discussions, enriching the dialogue, even though they lack the voting privilege on resolutions
3)What is a negative vote by one of the permanent members of the Security Council known as?
Ans:A unique power within the United Nations Security Council is the “veto,” which allows any one of its five permanent members to unilaterally block the adoption of a “substantive” resolution. These five nations—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—wield immense influence due to this privilege. Should any one of them cast a negative vote, even if the vast majority of other Council members support the resolution, it will not pass. It’s important to note that this potent veto power is reserved for substantive matters and does not extend to procedural votes.
4)Why was the Trusteeship Council established?
Ans:The UN’s Trusteeship Council was created to supervise Trust Territories, which were former colonies or mandates unprepared for self-governance post-WWII. Its main objective was to advance these territories politically, economically, socially, and educationally, paving their way to self-determination.
5)Why did the UN impose economic sanctions against the South African government?
Ans:Economic sanctions played a vital role in dismantling South African apartheid. By imposing trade and financial restrictions, the international community created significant economic hardship for the regime. This external pressure, coupled with robust internal resistance, made the continuation of discriminatory policies unsustainable. Ultimately, these combined forces compelled the South African government to negotiate, leading to Nelson Mandela’s release and the nation’s transition to democracy
6)What is the relevance of the UN in today’s world?
Ans:The contemporary global landscape urgently calls for a revitalized United Nations. To effectively address today’s conflicts and imbalances, the UN must undergo significant reforms. This transformation is crucial for it to become a more potent force for peace, capable of mending divisions and fostering a more stable and harmonious world.
F. Answer the following questions briefly:
1)The magnitude and scale of destruction during the Second World War created a great revulsion for war and a passionate yearning for peace.
In this context, explain:
(a) The signing of the Atlantic Charter
(b) The basic rights or the four freedoms guaranteed by the charter
(c) The San Francisco Conference and the establishment of the United Nations
Ans:(a)Though the United States had not yet officially entered World War II, the Atlantic Charter was a pivotal joint declaration outlining a vision for the post-war world. It expressed the shared goals of the two leaders, emphasizing principles such as self-determination for all peoples, freedom of the seas, global economic cooperation, and the renunciation of territorial aggression. Essentially, it laid the groundwork for a new international order based on peace, security, and human rights, aiming to address the root causes of conflict and foster a more stable future. It served as an early blueprint for what would eventually become the United Nations.
(b)Following the end of the conflict, a worldwide agreement solidified around the idea that everyone deserves certain basic safeguards, frequently encapsulated in what became known as the “Four Freedoms.” These crucial entitlements were articulated as: the right to be free from want, meaning access to life’s essentials; the right to freedom of speech, which protects the ability to voice one’s opinions; the right to freedom of religious belief, ensuring the liberty to practice one’s chosen faith; and the right to be free from fear, offering security from violence and persecution.
(c)In June 1945, a landmark event unfolded in San Francisco as delegates from fifty nations convened to sign the Atlantic Charter. This pivotal agreement served as the foundational document for a new international organization. Although absent from this initial gathering, Poland later became a signatory, expanding the total count of original member states to fifty-one. The official birth of the United Nations then occurred on October 24, 1945. This momentous date, recognized each year as United Nations Day, signified the launch of an institution committed to averting future conflicts and upholding fundamental human rights worldwide.
2)With reference to the United Nations discuss:
(a) The UN flag
(b) Any four objectives of the UN outlined in the Preamble of the UN Charter
(c) The obligations of all nations that follow from these objectives
Ans:(a) The United Nations flag is a carefully designed emblem, loaded with meaning to reflect the organization’s primary goals. Central to its design is a white depiction of the world, serving as a powerful symbol of global unity and the interconnectedness of all nations. Flanking this global map are two upward-curving olive branches, also rendered in white. The olive branch has long been recognized as a symbol of peace, its origins stretching back to antiquity. Their upward sweep on the flag suggests a forward-looking perspective and an optimistic vision for a world free from strife. These elements are all positioned against a serene, light blue background. This particular shade of blue is frequently linked with tranquility and the boundless expanse of the sky, further underscoring the flag’s message of international harmony and collective hopes for a peaceful future.
(b)The foundational principles guiding the UN are clearly articulated in the Preamble of the UN Charter. These objectives are multifaceted, aiming to create a more stable and equitable world. Primarily, the UN strives to maintain international peace and security, preventing conflicts and promoting peaceful resolutions. It also seeks to foster friendly relations among nations, emphasizing the principle of equality among all member states.Furthermore, the UN is dedicated to facilitating cooperation on global issues. This includes addressing economic, social, cultural, and humanitarian challenges that transcend national borders. A crucial objective is the promotion of human rights for all individuals, everywhere. Ultimately, the UN serves as a central platform, providing a forum for nations to collaborate and achieve these shared goals, with the overarching aim of preventing future wars.
(c)The UN Charter establishes a framework where all member nations, irrespective of their size or power, are considered equal and are bound by its provisions. This signifies a commitment from each member to adhere to the Charter’s principles. A cornerstone of this commitment is the expectation that all disputes between nations will be resolved peacefully, through negotiation, mediation, or other non-violent means. Crucially, member states are obligated to refrain from the use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state, except in cases of self-defense as outlined by the Charter.
3)With reference to the General Assembly and Security Council of the UN, answer the following questions:
(a) Mention any four functions of the General Assembly.
(b) Explain the veto power of the permanent members of the Security Council. What happens when the Security Council cannot take any action because of the veto?
(c) State three important functions of the Security Council.
Ans:(a)Problem Solving & Peacekeeping: It serves as a global forum for discussing international issues, offering recommendations for their resolution, and promoting the peaceful settlement of disputes.
Financial Oversight: The Assembly is responsible for considering and approving the UN’s budget, effectively controlling the organization’s financial resources.
Electoral Responsibilities: It elects non-permanent members to the Security Council, as well as members for the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) and the Trusteeship Council.
Supervisory Role: The General Assembly oversees the activities of other UN organs, ensuring coordination and accountability within the system.
Crisis Intervention: Under the “Uniting for Peace Resolution,” it can recommend “collective measures, including the use of armed forces,” in situations where the Security Council is deadlocked, enabling action during crises
(b)A single “no” vote from any permanent member of the Security Council can kill a resolution—this is the veto power. If a veto blocks Security Council action, the General Assembly can then step in, taking necessary measures to restore global peace.
(c)The Security Council plays a crucial role in maintaining global peace and security. Its primary functions include:
- Investigating Disputes: It examines international disputes and suggests peaceful resolutions.
- Imposing Sanctions: It can direct member states to implement economic sanctions against countries that commit aggression.
- Authorizing Military Action: When essential, it has the authority to deploy military force against an aggressor.
4)With reference to the organs of the UN, discuss:
(a) Any three functions of the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
(b) The composition and functions of the International Court of Justice
(c) Any four significant achievements of the UN
Ans:(a) Functions of the ECOSOC:The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) acts as the primary forum for global discussions on economic, social, and environmental matters. It champions international development, advances human rights, and addresses pressing global challenges such as health disparities, illiteracy, drug abuse, unemployment, and gender inequality. ECOSOC also coordinates the efforts of UN specialized agencies like WHO, UNESCO, UNICEF, ILO, and FAO to ensure a unified approach to global progress.
(b)The International Court of Justice (ICJ) consists of 15 judges, each elected for a nine-year term. These judges are chosen by both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council, with a critical rule: no two judges can be from the same nation. The ICJ’s main roles involve settling legal disagreements between UN member states and offering advisory opinions to other UN bodies.
(c) While not always preventing conflict, the UN has played a crucial role in restoring peace (e.g., Korean War, Suez Crisis, Gulf War) and facilitating national independence (e.g., Indonesia, Algeria, Morocco). Its economic sanctions were instrumental in ending apartheid in South Africa. The UN has consistently championed human rights, advocated for nuclear disarmament, and promoted peaceful nuclear energy. Through its specialized agencies, it has made significant strides in combating poverty, ignorance, malnutrition, hunger, and disease, with notable achievements in labor, health, child welfare, and education.
G Picture Study:
This building is the headquarters of an international organization which was established in October 1945 to maintain international peace and security
1)Name the organization.
Ans. The United Nations (UN), founded in 1945 by 51 countries after World War II, strives to uphold global peace and security, cultivate positive international relations, and encourage worldwide collaboration on pressing issues. Now with 193 member states, the UN operates on principles of sovereign equality, peaceful dispute resolution, and non-aggression. Its main bodies—the General Assembly, Security Council, Economic and Social Council, International Court of Justice, and Secretariat—work together to achieve its broad goals.
2)Where are the headquarters of this organization located?
Ans. New York City, often called the “Big Apple,” is a bustling global hub recognized for its distinctive skyline, diverse culture, and lively ambiance. It features famous landmarks like Times Square, the Statue of Liberty, and Central Park, alongside a thriving arts scene, major financial centers, and countless dining experiences.
3)Mention four important objectives of this organization.
Ans. The UN Charter’s Preamble outlines the organization’s foundational goals: upholding international peace and security, cultivating friendly relations among nations, advancing global cooperation on economic, social, cultural, and humanitarian matters, championing human rights and fundamental freedoms, acting as a central forum for national endeavors, and averting future conflicts.
4)Name three major organs of this organization.
Ans: The United Nations functions through several principal organs. The General Assembly is the chief deliberative and policymaking body, granting equal representation and a single vote to all 193 member states. It serves as a global platform for discussing international issues, approving the UN budget, and electing members to other councils.
It comprises 15 members: five permanent (China, France, Russia, the UK, and the US) with veto power, and ten non-permanent members elected for two-year terms. The Council can investigate disputes, recommend resolutions, impose sanctions, and authorize military force, with its decisions being legally binding.
The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) acts as the central hub for addressing global economic, social, and environmental challenges. Composed of 54 member states, ECOSOC coordinates the work of various UN agencies and programs, focusing on policy recommendations for improving living standards, employment, and international cooperation in areas like health, education, and human rights