1. What is Photosynthesis?
It is the process by which green plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (food) and oxygen.
Word Equation: Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen (in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll)
Chemical Equation: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
2. Key Requirements
Sunlight: Source of energy.
Chlorophyll: Green pigment in chloroplasts that traps light energy.
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Enters the leaf through tiny pores called stomata.
Water (H₂O): Absorbed from the soil by roots and transported to the leaves.
3. Main Steps of Photosynthesis
Light Reaction (Photochemical Phase):
Occurs in the grana of chloroplasts.
Requires light.
Products: Oxygen (released as a by-product), ATP (energy currency), and NADPH (a reducing agent).
Dark Reaction (Biosynthetic Phase):
Occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts.
Does not require light directly (uses the products from the light reaction).
Uses the ATP and NADPH to convert CO₂ into glucose.
The process of carbon fixation (e.g., the Calvin Cycle) produces sugar.
4. Importance of Photosynthesis
Food Production: It is the ultimate source of food for all living organisms.
Oxygen Supply: It releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is essential for respiration.
Energy Storage: It converts solar energy into chemical energy stored in food.
5. Experiments to Understand Photosynthesis
Starch Test: Used to confirm photosynthesis. A positive iodine test (blue-black colour) shows the presence of starch, which is a product of photosynthesis.
Destarching: Before any experiment, a plant is kept in darkness for 48 hours to remove stored starch. This ensures that any starch tested for was made during the experiment.
Key experiments prove that:
Light is necessary (partially covered leaf does not produce starch in covered part).
Chlorophyll is necessary (variegated leaf produces starch only in green parts).
Carbon Dioxide is necessary (using KOH to absorb CO₂).
6. Factors Affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis
Light Intensity: Increases rate up to a point.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration: Major limiting factor; increases rate up to a point.
Temperature: An optimum temperature (around 25-35°C) is required. Very high or low temperatures slow down the process.
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
1) The production of starch, and not glucose, is often used as a measure of photosynthesis in leaves because
(a) starch is the immediate product of photosynthesis.
(b) glucose formed in photosynthesis soon gets converted into starch.
(c) starch is soluble in water.
(d) sugar cannot be tested.
Ans:(b) glucose formed in photosynthesis soon gets converted into starch.
2)The number of water molecules required in the chemical reactions to produce one molecule of glucose during photosynthesis is:
(a) six
(b) twelve
(c) eighteen
(d) twenty-four
Ans:(b) twelve
3)The rate of photosynthesis is NOT affected by:
(a) light intensity
(b) humidity
(c) temperature
(d) CO2 concentration
Ans:(b) humidity
4)Chlorophyll in a leaf is required for
(a) breaking down water into hydrogen and oxygen.
(b) emitting green light.
(c) trapping light energy.
(d) storing starch in the leaves.
Ans: (c) trapping light energy.
5)If the rate of respiration becomes more than the rate of photosynthesis, plants will:
(a) continue to live, but will not be able to store food.
(b) be killed instantly.
(c) grow more vigorously because more energy will be available.
(d) stop growing and die gradually of starvation.
Ans:(a) continue to live, but will not be able to store food.
6)Which chemical reaction occurs during photosynthesis?
(a) Carbon dioxide is reduced and water is oxidised.
(b) Water is reduced and carbon dioxide is oxidised.
(c) Both carbon dioxide and water are oxidised.
(d) Both carbon dioxide and water are reduced.
Ans: (a) Carbon dioxide is reduced and water is oxidised.
7)The specific function of light energy in the process of photosynthesis is:
(a) reduce carbon dioxide.
(b) synthesize glucose.
(c) activate chlorophyll.
(d) split water molecule.
Ans:(d) split water molecule.
8)A plant is kept in a dark cupboard for about 48 hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis in order to:
(a) remove chlorophyll from the leaves.
(b) remove starch from the leaves.
(c) ensure that no photosynthesis occurred.
(d) ensure that the leaves are free from starch.
Ans:(d) ensure that the leaves are free from starch.
9)During photosynthesis, the oxygen in glucose comes from
(a) CO2
(b) water
(c) both CO2 and water
(d) oxygen via air
Ans:(a) CO2
B. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Name the following:
(a) The category of organisms that prepare their own food from basic raw materials.
(b) The kind of plastics found in the mesophyll cells of the leaf.
(c) The compound which stores energy in the cells.
(d) The first form of food substance produced during photosynthesis.
(e) The organisms that can be called “natural purification” of the leaf.
(f) The source of CO2 for aquatic plants.
(g) The part of chloroplast where the dark reaction of photosynthesis takes place.
(h) The tissues that transport manufactured type of starch from leaves to all parts of the plants.
Ans:
a) Autotrophs
(b) Chloroplasts
(c) ATP (or Adenosine Triphosphate)
(d) Glucose
(e) Green plants
(f) Dissolved CO₂ in water (or Carbonates/Bicarbonates)
(g) Stroma
(h) Phloem
C. SHORT ANSWER TYPE
1)Mention one difference between the following on the basis of what is given in brackets.
(a) Respiration and photosynthesis (gas released).
(b) Light and dark reactions (produce formed).
(c) Problems and consumers (mode of nutrition).
(d) Grass and grasshopper (mode of nutrition).
(e) Chlorophyll and chloroplast (part of plant cell).
Ans:
(a) Respiration and photosynthesis (gas released).
The key difference in the gas released is that the process of respiration primarily releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as a waste product. In contrast, the process of photosynthesis releases oxygen, which is a vital by-product for most living organisms. Essentially, respiration consumes oxygen and produces carbon dioxide, while photosynthesis does the reverse, using carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
(b) Light and dark reactions (product formed).
A fundamental difference lies in the initial products they form. The light-dependent reactions, which require sunlight, do not produce sugar directly. Instead, they create energy-carrying molecules, specifically ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions (light-independent reactions), on the other hand, use this chemical energy (ATP and NADPH) to produce the actual sugar molecule, glucose, from carbon dioxide.
(c) Producers and consumers (mode of nutrition).
The primary difference in their mode of nutrition is that producers, such as green plants, are autotrophic. This means they can synthesize their own food from simple inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water using sunlight. Consumers, however, are heterotrophic; they cannot make their own food and must obtain their energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms, either producers or other consumers.
(d) Grass and grasshopper (mode of nutrition).
Grass, being a plant, is an autotroph. It manufactures its own food through the process of photosynthesis. A grasshopper, being an animal, is a consumer (specifically, a herbivore). It has a heterotrophic mode of nutrition, meaning it gets its energy and organic materials by consuming autotrophs like grass.
(e) Chlorophyll and chloroplast (part of plant cell).
The main difference is their structural relationship within the plant cell. Chlorophyll is not a structure itself, but a green pigment. It is a molecule that is embedded within the membranes of the chloroplast. The chloroplast, however, is a large, membrane-bound organelle. It is the specific part of the cell that contains the chlorophyll and is the actual site where photosynthesis takes place. So, chlorophyll is a component inside the chloroplast.
2)Identify the false statements and rewrite them correctly by changing the first or the last word only.
(a) Dark reaction of photosynthesis occurs during night time.
(b) Immediate product of photosynthesis is glucose.
(c) Stark products in a leaf remains stored in it for 2-3 weeks before it is used by other parts of the plant.
(d) Photosynthesis requires enzymes.
(e) Green plants are consumers.
(f) Photosynthesis results in loss of dry weight of the plant.
(g) Photosynthesis stops at a temperature of about 35°C.
(h) Photosynthesis occurs only in cells containing chloroplasts.
(i) Green plants perform photosynthesis.
(j) Algae are anorexophs.
Ans:
(a) False
Corrected: Light reaction of photosynthesis occurs during night time.
(OR)
Dark reaction of photosynthesis occurs during day time.
(b) False
Corrected: Immediate product of photosynthesis is sugar.
(OR)
End product of photosynthesis is glucose.
(c) False (Assuming “Stark” is a typo for “Starch”)
Corrected: Starch products in a leaf remain stored for a short time before use.
(d) True – This statement is correct.
(e) False
Corrected: Green plants are producers.
(f) False
Corrected: Photosynthesis results in gain of dry weight of the plant.
(g) False
Corrected: Photosynthesis slows down at a temperature of about 35°C.
(h) True – This statement is essentially correct.
(i) True – This statement is correct.
(j) False (Assuming “anorexophs” is a typo)
Corrected: Algae are autotrophs.
3) Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answer from the choices given in the brackets.
(a) The site of light reaction in the cells of a leaf is …… (cytoplasm, stroma, grana).
(b) The chemical substance used to test the presence of starch in the cell of a leaf is …… (CaCl₂, iodine solution, Benedict solution).
(c) Stroma is the ground substance in …… (cytoplasm, chloroplast, ribosomes).
(d) The dark reaction of photosynthesis is known as …… (Hill reaction, cyclic phosphorylation, Calvin cycle).
(e) In the flowering plants, food is transported in the form of …… (sucrose, glucose, starch).
(a) grana
(b) iodine solution
(c) chloroplast
(d) Calvin cycle
(e) sucrose
4)Are the following statements true or false? Give reason in support of your answer.
(a) The rate of photosynthesis continues to rise as long as the intensity of light rises.
(b) The outside atmospheric temperature has no effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
(c) If you immerse a leaf intact on the plant in ice cold water, it will continue to photosynthesize in bright sunshine.
(d) Destarching of the leaves of a potted plant can occur only at night.
(e) The starting point of carbon cycle is the release of CO₂ by animals during respiration.
(f) If a plant is kept in bright light all the 24 hours for a few days, the dark reaction (biosynthetic phase) will fail to occur.
(g) Photosynthesis is considered as a process supporting all life on earth.
Ans:
(a) False.
The rate of photosynthesis rises with light intensity only up to a certain point (the light saturation point). Beyond this, other factors like CO₂ concentration or temperature become limiting, and the rate does not increase further.
(b) False.
Temperature has a significant effect on the rate of photosynthesis because it influences the enzymes involved in the process. The rate increases up to an optimum temperature and then declines.
(c) False.
Extremely low temperature (ice cold water) inactivates the enzymes required for photosynthesis. Therefore, the process will slow down or stop, even in bright sunshine.
(d) False.
Destarching (using up stored starch) occurs whenever the plant is respiring but not photosynthesizing. This primarily happens at night, but it can also occur during the day if the plant is kept in complete darkness.
(e) False.
The carbon cycle is a continuous process with no single starting point. While animal respiration releases CO₂, this CO₂ was originally fixed from the atmosphere by plants during photosynthesis. A more accurate view is that the cycle involves the continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, organisms, and the earth.
(f) False.
The dark reaction (Calvin cycle) is dependent on the products of the light reaction (ATP and NADPH), not on the absence of light. If the plant is in bright light, the light reactions will occur and provide the necessary energy, allowing the dark reaction to proceed.
(g) True.
It produces oxygen and is the original source of energy for nearly all food chains, thereby directly or indirectly supporting almost all life on Earth.
3) Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answer from the choices given in the brackets.
(a) The site of light reaction in the cells of a leaf is …… (cytoplasm, stroma, grana).
(b) The chemical substance used to test the presence of starch in the cell of a leaf is …… (CaCl₂, iodine solution, Benedict solution).
(c) Stroma is the ground substance in …… (cytoplasm, chloroplast, ribosomes).
(d) The dark reaction of photosynthesis is known as …… (Hill reaction, cyclic phosphorylation, Calvin cycle).
(e) In the flowering plants, food is transported in the form of …… (sucrose, glucose, starch).
(a) grana
(b) iodine solution
(c) chloroplast
(d) Calvin cycle
(e) sucrose
4)Are the following statements true or false? Give reason in support of your answer.
(a) The rate of photosynthesis continues to rise as long as the intensity of light rises.
(b) The outside atmospheric temperature has no effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
(c) If you immerse a leaf intact on the plant in ice cold water, it will continue to photosynthesize in bright sunshine.
(d) Destarching of the leaves of a potted plant can occur only at night.
(e) The starting point of carbon cycle is the release of CO₂ by animals during respiration.
(f) If a plant is kept in bright light all the 24 hours for a few days, the dark reaction (biosynthetic phase) will fail to occur.
(g) Photosynthesis is considered as a process supporting all life on earth.
Ans:
(a) False.
The rate of photosynthesis rises with light intensity only up to a certain point (the light saturation point). Beyond this, other factors like CO₂ concentration or temperature become limiting, and the rate does not increase further.
(b) False.
Temperature has a significant effect on the rate of photosynthesis because it influences the enzymes involved in the process. The rate increases up to an optimum temperature and then declines.
(c) False.
Extremely low temperature (ice cold water) inactivates the enzymes required for photosynthesis. Therefore, the process will slow down or stop, even in bright sunshine.
(d) False.
Destarching (using up stored starch) occurs whenever the plant is respiring but not photosynthesizing. This primarily happens at night, but it can also occur during the day if the plant is kept in complete darkness.
(e) False.
The carbon cycle is a continuous process with no single starting point. While animal respiration releases CO₂, this CO₂ was originally fixed from the atmosphere by plants during photosynthesis. A more accurate view is that the cycle involves the continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, organisms, and the earth.
(f) False.
The dark reaction (Calvin cycle) is dependent on the products of the light reaction (ATP and NADPH), not on the absence of light. If the plant is in bright light, the light reactions will occur and provide the necessary energy, allowing the dark reaction to proceed.
(g) True.
It produces oxygen and is the original source of energy for nearly all food chains, thereby directly or indirectly supporting almost all life on Earth.
5)Given below are five terms. Rewrite the terms in the correct order so as to be in logical sequence with regard to photosynthesis: (i) water molecules, (ii) oxygen, (iii) grana, (iv) hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, (v) photons.
Ans: (v) photons → (iii) grana → (i) water molecules → (iv) hydrogen and hydroxyl ions → (ii) oxygen
6) State any four differences between photosynthesis and respiration.
Ans:Process: Photosynthesis builds up glucose (anabolic), while respiration breaks down glucose (catabolic).
Energy: Photosynthesis stores energy, while respiration releases energy.
Gas Exchange: Photosynthesis uses CO₂ and releases O₂, while respiration uses O₂ and releases CO₂.
Site: Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, while respiration occurs in mitochondria.
7) “Oxygen is a waste product of photosynthesis.” Comment.
Ans: Yes, oxygen is a waste product of photosynthesis. The process uses sunlight to split water molecules to obtain hydrogen for making food (glucose). The oxygen from the water is not needed by the plant and is released into the air.
8) Why is it necessary to place a plant in the dark before starting an experiment on photosynthesis? Explain.
Ans:The plant is placed in the dark to destarch it. In the absence of light, photosynthesis stops, and the plant uses up its stored starch. This ensures that any starch found later in the experiment was produced during the experiment and not before.
9) In most of the experiments on photosynthesis, we use a de-starched leaf or plant. What is the purpose of de-starching?
Ans:We de-starch a plant to clear out any stored starch made earlier. This way, when we test the leaves after our experiment, any starch we find must have been produced during the test. It proves that our experiment directly caused the photosynthesis that made the starch.
10) Why is it not possible to demonstrate respiration in a green plant kept in sunlight?
Ans:In sunlight, a green plant is both photosynthesizing and respiring at the same time.
Photosynthesis is very fast and releases a large amount of oxygen.Respiration uses a small amount of oxygen and produces carbon dioxide.The oxygen produced by photosynthesis is so much that it completely masks the oxygen being used by respiration. At the same time, the carbon dioxide released by respiration is immediately absorbed and used up for photosynthesis.Because of this, the gas exchange from respiration (taking in O₂ and releasing CO₂) is hidden by the much larger, opposite gas exchange of photosynthesis (taking in CO₂ and releasing O₂). This is why we cannot observe respiration in a green plant while it is in sunlight.
11) Most leaves have the upper surface more green and shiny than the lower one. Why?
Ans: The top of a leaf is a masterpiece of efficient design, built for one main job: photosynthesis. Two key features make this possible.
First, just beneath the surface, are the palisade cells. These tall, tightly-packed cells act like a solar panel farm. They are filled with tiny structures called chloroplasts, which contain the green pigment chlorophyll. By positioning this dense, light-absorbing layer right at the top, the plant captures the sun’s energy with maximum efficiency the moment it hits the leaf.
Protecting this operation is the second feature: the waxy cuticle. This is the clear, waterproof coating you see when water beads up on a leaf. Its main job is to prevent the plant from losing too much water through evaporation, which is crucial for its survival. This waxy layer also gives the leaf its shiny look and helps shield it from dust, mold, and some pests.
In short, the leaf’s upper surface works like a perfectly managed factory: the palisade cells are the power generators inside, and the waxy cuticle is the protective, water-saving shell on the outside.
12) How would you demonstrate that green plants release oxygen when exposed to light?
Ans:When a water plant such as Hydrilla is placed in a beaker of water and covered with an inverted funnel, a test tube filled with water is placed over the funnel’s stem.
On exposing this setup to bright light, the plant undergoes photosynthesis. This process produces gas bubbles, which rise and collect in the test tube.
The collected gas can be tested by inserting a glowing wooden splinter. The splinter reignites, proving that the gas is oxygen.
13) Describe the main chemical changes which occur during photosynthesis in
(i) Light reaction
(ii) Dark reaction.
Ans : (i) Light Reaction:
Occurring in the grana, this stage uses chlorophyll to capture sunlight. The light energy splits water molecules, releasing oxygen and producing energy-rich compounds (ATP and NADPH).
(ii) Dark Reaction:
Taking place in the stroma, this phase uses the ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. It is called the dark reaction because it does not directly need light to proceed.
14) Complete the following food chains by writing the names of appropriate organisms in the blanks.
(i) Grass → …… → Snake → ……
(ii) …… → Mouse …… → Peacock
Ans: (i) Grass → …Grasshopper… → Snake → …Eagle/Hawk…
(ii) …Corn/Grain… → Mouse → …Snake… → Peacock
15)How do non-green plants such as fungi and bacteria obtain their nourishment?
Ans: Non-green plants like fungi and bacteria are heterotrophs. They obtain their nourishment by:
Saprophytic Nutrition: Feeding on dead and decaying organic matter (e.g., most fungi, some bacteria).
Parasitic Nutrition: Deriving food from a living host organism, often harming it (e.g., rust fungus, pathogenic bacteria).
16)All life owes its existence to chlorophyll. Give reason.
Ans: Chlorophyll is the green pigment that drives photosynthesis. This single process allows plants to create the food that starts our food chains and the oxygen that fills our air. Essentially, this one molecule supports almost all life on Earth.
17)Complete the following by filling the blanks 1 to 5 with appropriate words/terms/phrases:
To test the leaf for starch, the leaf is boiled in water to …… (1). It is next boiled in methylated spirit to …… (2). The leaf is placed in warm water to soften it. It is then placed in a dish and …… (3) solution is added. The region, which contains starch, turns …… (4) and the region, which does not contain starch, turns …… (5).
Ans:
To test the leaf for starch, the leaf is boiled in water to …kill the cells and break down the cell membranes… (1). It is next boiled in methylated spirit to …remove the chlorophyll… (2). The leaf is placed in warm water to soften it. It is then placed in a dish and …iodine… (3) solution is added. The region, which contains starch, turns …blue-black… (4) and the region, which does not contain starch, turns …brownish-yellow… (5).
D. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION SKILL TYPE
1)A candidate studied the importance of certain factors in photosynthesis. He took a potted plant and kept it in the dark for over 24 hours. In the early hours of the next morning, he covered one of the leaves with dark paper in the centre only. Then he placed the plant in sunlight for a few hours and tested the leaf which was covered with black paper for starch.
(a) What aspect of photosynthesis was being investigated?
(b) Is there any control in this experiment? If so, state it.
(c) Why was the plant kept in the dark before the experiment?
(d) Describe step by step, how the candidate proceeded to test the leaf for the presence of starch.
Ans: (a) The experiment was investigating whether light is necessary for photosynthesis to occur and for starch production.
(b) Yes, there is a control in this experiment. The uncovered parts of the same leaf that were exposed to sunlight act as the control. These parts should test positive for starch, confirming that the plant is capable of photosynthesis under normal light conditions.
(c) The plant was kept in the dark before the experiment to remove or use up all the stored starch from its leaves. This process is called destarching. It ensures that any starch found later in the experiment was produced during the experimental period and not stored beforehand.
(d) The candidate tested the leaf for starch using the iodine test as follows:
The covered leaf was plucked from the plant.
The dark paper was carefully removed.
The leaf was boiled in water for a few minutes to break down the cell walls and make it soft.
The leaf was then placed in a beaker of boiling methylated spirit (alcohol) using a water bath. This step dissolves the chlorophyll, turning the leaf pale or whitish, which makes the colour change easier to see.
The brittle leaf was dipped back into warm water to soften it again.
The leaf was spread flat on a tile or dish, and a few drops of iodine solution were added to it.
The region that had been covered by the paper (and did not receive light) remained pale or turned brownish (negative for starch).
The region that was exposed to sunlight turned a blue-black colour, indicating the presence of starch.
2) Photosynthesis in green plants is directly and indirectly dependent on so many plant structures. Explain briefly the role of the following structures in this process.
(a) Guard cells
(b) Cuticle
c)Mesophyll Cells
d) Xylem Tissue in leaf Veins
e)pholem Tissue in leaf Veins
f) stomata
Ans:
(a) Guard Cells
These are two bean-shaped cells that surround each stoma. They control the opening and closing of the stomatal pore. They open to let carbon dioxide in for photosynthesis and close to prevent water loss.
(b) Cuticle
This is the waxy, waterproof layer covering the leaf. Its main role is to prevent water loss from the leaf surface, ensuring the plant doesn’t dry out, which is essential for maintaining the processes that support photosynthesis.
(c) Mesophyll Cells
These are the main photosynthetic cells inside the leaf. The palisade mesophyll cells, packed with chloroplasts, are the primary site for capturing light and performing photosynthesis. The spongy mesophyll has air spaces that help in the exchange of gases like CO₂ and O₂.
(d) Xylem Tissue in Leaf Veins
The xylem acts like a pipeline. It transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots up to the leaves. This water is a crucial raw material for photosynthesis and also helps keep the plant cells rigid.
(e) Phloem Tissue in Leaf Veins
The phloem is the transport system for the food created by photosynthesis. It carries the sugars (glucose) produced in the leaf to other parts of the plant that need it for energy and growth.
(f) Stomata
These are tiny pores, mostly on the underside of the leaf. They are the entry points for carbon dioxide, a key ingredient for photosynthesis. They are also the main sites for the exit of oxygen (a by-product) and water vapor (transpiration).
3)Given below is a schematic diagram to illustrate some aspects of photosynthesis.
(a) Fill up the gaps, in blank spaces (1-4), by writing the names of the correct items.
(b) What phenomenon do the thick arrows A and B indicate respectively?
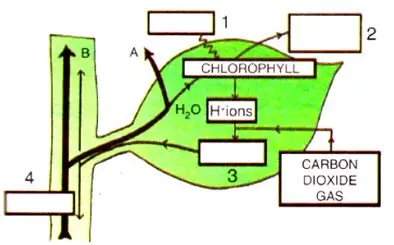
Ans:
(a) Fill in the gaps (1-4):
Sunlight / Light Energy
Oxygen (O₂)
Water (H₂O)
Glucose / Carbohydrates
(b) Phenomenon indicated by thick arrows A and B:
Arrow A: Light Absorption. It indicates chlorophyll absorbing light energy from the sun.
Arrow B: Gas Exchange. It indicates the release of oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis.
4)Given below is the representation of a certain phenomenon in nature, with four organisms 1-4.
Ans:
The four organisms are:
Plant (Producer)
Grasshopper (Primary Consumer/Herbivore)
Frog (Secondary Consumer/Carnivore)
Eagle (Tertiary Consumer/Top Carnivore)
The flow of energy and food is: Plant → Grasshopper → Frog → Eagle.
5)Enumerate the steps involved in testing a green leaf for the presence of starch.
Ans:Steps to Test a Leaf for Starch:
Boil the Leaf: Dip the leaf in boiling water for a minute. This softens it and breaks down the cell walls.
Turn Off the Burner. For safety, extinguish the burner before the next step.
Use Alcohol: Place the leaf in a beaker of warm alcohol (using a water bath). This removes the green chlorophyll, turning the leaf pale or white.
Rinse and Soften: Carefully take the leaf out of the alcohol, rinse it in warm water, and lay it flat on a tile.
Add Iodine: Add a few drops of iodine solution onto the leaf.
Observe the Result: If starch is present, the areas where it exists will turn a blue-black color. A brownish-yellow color means no starch is present.
6)Given alongside is the diagram of an experimental set-up :
(a) What is the objective of this experiment?
(b) Will it work satisfactorily? Give reason.
(c) What alteration(s) will you make in it for obtaining expected result?
(d) Would you take any step before starting the experiment? Describe this step and explain its necessity.
(a) Objective of the experiment:
To show that carbon dioxide (CO₂) is necessary for photosynthesis.
(b) Will it work satisfactorily?
No, it will not work well.
Reason:
The flask contains lime water (which absorbs CO₂), but the air around the plant still has plenty of CO₂. The plant can use this CO₂ from the surrounding air to perform photosynthesis, so we cannot prove that the gas inside the flask was necessary.
(c) Alteration for expected result:
Place the entire plant inside a large, transparent plastic bag along with the flask. This setup will remove all CO₂ from the air around the entire plant, creating a controlled environment.
(d) Yes, a crucial step before starting is to destarch the plant.This is done by placing the plant in a dark cupboard or room for about 48 hours.This step is necessary to remove all the pre-existing starch from the leaves. If this isn’t done, any starch detected at the end of the experiment could be old starch, and we wouldn’t know if our experiment actually produced it. Destarching ensures that any starch we find later was made only during the experimental conditions.
7)Draw a neat diagram of the stomatal apparatus found in the epidermis of leaves and label the Stoma, Guard cells, Chloroplast, Epidermal cells, Cell wall and Nucleus.
Ans: A neat diagram of the stomatal apparatus would show a section of the leaf’s epidermis.
In the center, draw an oval-shaped pore. This is the Stoma.
Surrounding the stoma, draw two bean-shaped cells. These are the Guard cells.
Inside each guard cell, draw a few small ovals to represent the Chloroplast.
Also inside each guard cell, draw a small circle to represent the Nucleus.
Draw the outer boundary of the guard cells as a bold line; this is the Cell wall.
Finally, around the guard cells, draw several irregular, jigsaw-puzzle-like shapes that fit together. These are the Epidermal cells.
This setup controls the exchange of gases and water vapor for the leaf.